注意
跳转到末尾 以下载完整示例代码。
次坐标轴#
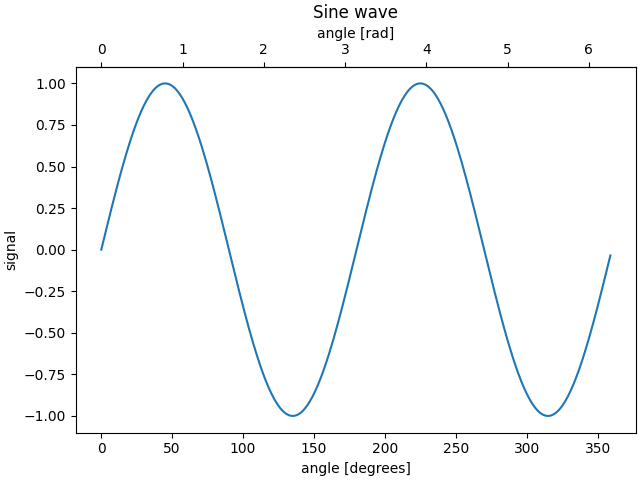
有时我们希望在绘图上添加一个次坐标轴,例如在同一张图上将弧度转换为角度。我们可以通过创建一个仅显示一个轴的子坐标轴来实现,使用 axes.Axes.secondary_xaxis 和 axes.Axes.secondary_yaxis。通过在 *functions* 关键字参数中提供正向和反向转换函数元组,此次坐标轴可以与主坐标轴具有不同的刻度。
import datetime
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.dates as mdates
fig, ax = plt.subplots(layout='constrained')
x = np.arange(0, 360, 1)
y = np.sin(2 * x * np.pi / 180)
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.set_xlabel('angle [degrees]')
ax.set_ylabel('signal')
ax.set_title('Sine wave')
def deg2rad(x):
return x * np.pi / 180
def rad2deg(x):
return x * 180 / np.pi
secax = ax.secondary_xaxis('top', functions=(deg2rad, rad2deg))
secax.set_xlabel('angle [rad]')
plt.show()
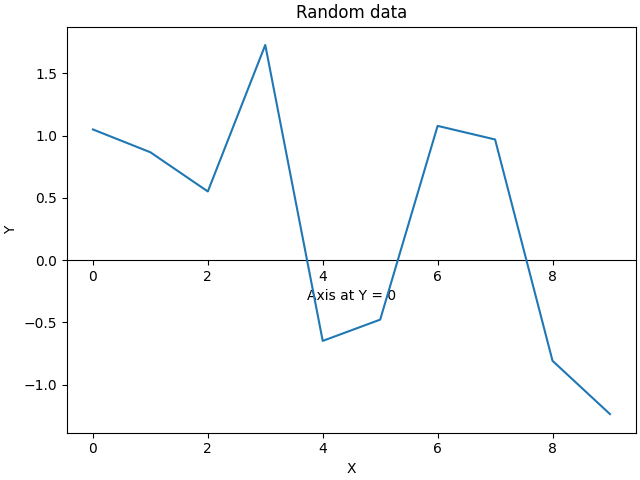
默认情况下,次坐标轴在 Axes 坐标空间中绘制。我们也可以提供自定义变换以将其放置在不同的坐标空间中。这里我们将坐标轴放置在数据坐标系中 Y = 0 的位置。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(layout='constrained')
x = np.arange(0, 10)
np.random.seed(19680801)
y = np.random.randn(len(x))
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.set_xlabel('X')
ax.set_ylabel('Y')
ax.set_title('Random data')
# Pass ax.transData as a transform to place the axis relative to our data
secax = ax.secondary_xaxis(0, transform=ax.transData)
secax.set_xlabel('Axis at Y = 0')
plt.show()
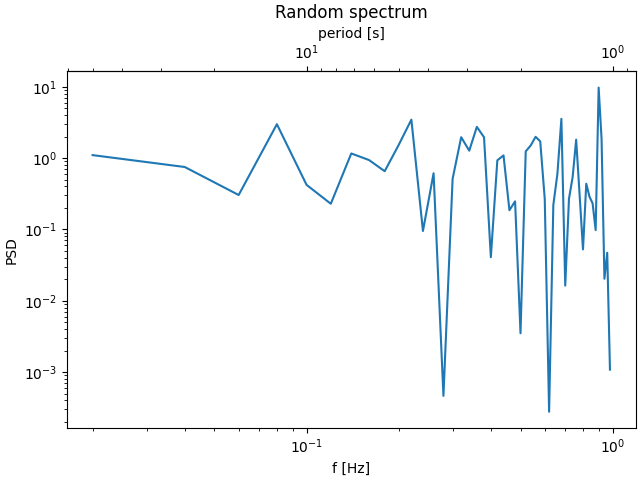
这是对数-对数刻度中波数到波长的转换示例。
注意
在这种情况下,父坐标轴的 x 刻度是对数的,因此子坐标轴也变为对数刻度。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(layout='constrained')
x = np.arange(0.02, 1, 0.02)
np.random.seed(19680801)
y = np.random.randn(len(x)) ** 2
ax.loglog(x, y)
ax.set_xlabel('f [Hz]')
ax.set_ylabel('PSD')
ax.set_title('Random spectrum')
def one_over(x):
"""Vectorized 1/x, treating x==0 manually"""
x = np.array(x, float)
near_zero = np.isclose(x, 0)
x[near_zero] = np.inf
x[~near_zero] = 1 / x[~near_zero]
return x
# the function "1/x" is its own inverse
inverse = one_over
secax = ax.secondary_xaxis('top', functions=(one_over, inverse))
secax.set_xlabel('period [s]')
plt.show()
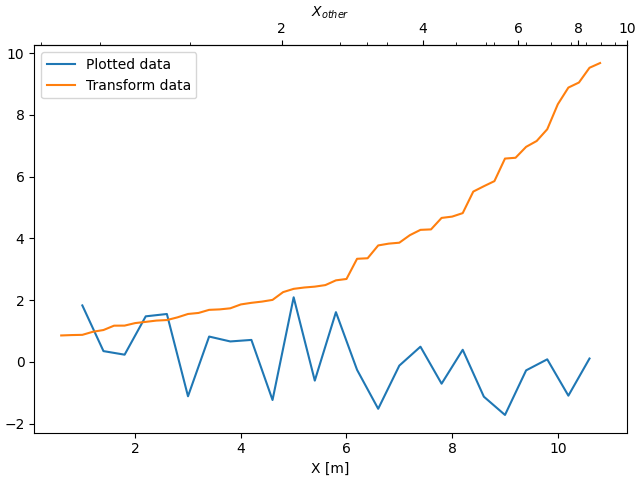
有时我们希望以数据中特设的,并凭经验推导的变换来关联坐标轴。或者,一个轴可能是另一个轴的复杂非线性函数。在这些情况下,我们可以将正向和反向变换函数设置为从一组独立变量到另一组独立变量的线性插值。
注意
为了正确处理数据边距,映射函数(本例中的 forward 和 inverse)需要定义在标称绘图限制之外。可以通过将插值扩展到绘图值之外(向左和向右),从而强制执行此条件,参见下面的 x1n 和 x2n。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(layout='constrained')
x1_vals = np.arange(2, 11, 0.4)
# second independent variable is a nonlinear function of the other.
x2_vals = x1_vals ** 2
ydata = 50.0 + 20 * np.random.randn(len(x1_vals))
ax.plot(x1_vals, ydata, label='Plotted data')
ax.plot(x1_vals, x2_vals, label=r'$x_2 = x_1^2$')
ax.set_xlabel(r'$x_1$')
ax.legend()
# the forward and inverse functions must be defined on the complete visible axis range
x1n = np.linspace(0, 20, 201)
x2n = x1n**2
def forward(x):
return np.interp(x, x1n, x2n)
def inverse(x):
return np.interp(x, x2n, x1n)
# use axvline to prove that the derived secondary axis is correctly plotted
ax.axvline(np.sqrt(40), color="grey", ls="--")
ax.axvline(10, color="grey", ls="--")
secax = ax.secondary_xaxis('top', functions=(forward, inverse))
secax.set_xticks([10, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100])
secax.set_xlabel(r'$x_2$')
plt.show()
最后一个示例将 np.datetime64 转换为 x 轴上的年日,并将 y 轴上的摄氏度转换为华氏度。请注意添加了第三个 y 轴,并且可以使用浮点数作为位置参数来放置它。
dates = [datetime.datetime(2018, 1, 1) + datetime.timedelta(hours=k * 6)
for k in range(240)]
temperature = np.random.randn(len(dates)) * 4 + 6.7
fig, ax = plt.subplots(layout='constrained')
ax.plot(dates, temperature)
ax.set_ylabel(r'$T\ [^oC]$')
ax.xaxis.set_tick_params(rotation=70)
def date2yday(x):
"""Convert matplotlib datenum to days since 2018-01-01."""
y = x - mdates.date2num(datetime.datetime(2018, 1, 1))
return y
def yday2date(x):
"""Return a matplotlib datenum for *x* days after 2018-01-01."""
y = x + mdates.date2num(datetime.datetime(2018, 1, 1))
return y
secax_x = ax.secondary_xaxis('top', functions=(date2yday, yday2date))
secax_x.set_xlabel('yday [2018]')
def celsius_to_fahrenheit(x):
return x * 1.8 + 32
def fahrenheit_to_celsius(x):
return (x - 32) / 1.8
secax_y = ax.secondary_yaxis(
'right', functions=(celsius_to_fahrenheit, fahrenheit_to_celsius))
secax_y.set_ylabel(r'$T\ [^oF]$')
def celsius_to_anomaly(x):
return (x - np.mean(temperature))
def anomaly_to_celsius(x):
return (x + np.mean(temperature))
# use of a float for the position:
secax_y2 = ax.secondary_yaxis(
1.2, functions=(celsius_to_anomaly, anomaly_to_celsius))
secax_y2.set_ylabel(r'$T - \overline{T}\ [^oC]$')
plt.show()
脚本总运行时间: (0 分钟 5.575 秒)