注意
转到末尾以下载完整示例代码。
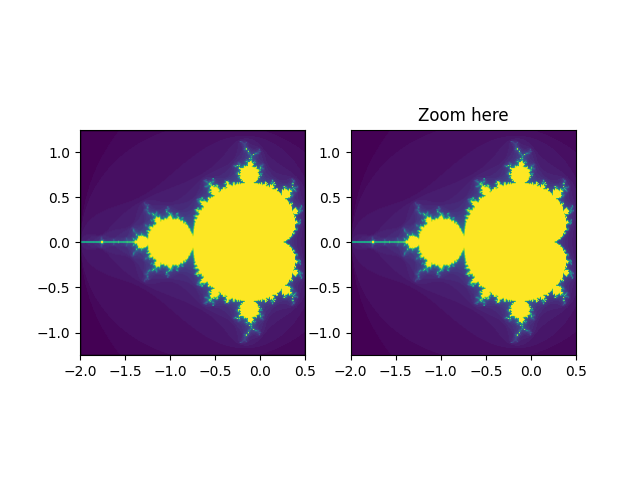
Viewlims#
创建两个相同的面板。放大右侧面板将在第一个面板中显示一个矩形,表示放大的区域。
注意
此示例展示了 Matplotlib 的交互功能,它不会出现在静态文档中。请在您的机器上运行此代码以查看交互性。
您可以复制粘贴部分内容,或使用页面底部的链接下载整个示例。
import functools
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.patches import Rectangle
# A class that will regenerate a fractal set as we zoom in, so that you
# can actually see the increasing detail. A box in the left panel will show
# the area to which we are zoomed.
class MandelbrotDisplay:
def __init__(self, h=500, w=500, niter=50, radius=2., power=2):
self.height = h
self.width = w
self.niter = niter
self.radius = radius
self.power = power
def compute_image(self, xlim, ylim):
self.x = np.linspace(*xlim, self.width)
self.y = np.linspace(*ylim, self.height).reshape(-1, 1)
c = self.x + 1.0j * self.y
threshold_time = np.zeros((self.height, self.width))
z = np.zeros(threshold_time.shape, dtype=complex)
mask = np.ones(threshold_time.shape, dtype=bool)
for i in range(self.niter):
z[mask] = z[mask]**self.power + c[mask]
mask = (np.abs(z) < self.radius)
threshold_time += mask
return threshold_time
def ax_update(self, ax):
ax.set_autoscale_on(False) # Otherwise, infinite loop
# Get the number of points from the number of pixels in the window
self.width, self.height = ax.patch.get_window_extent().size.round().astype(int)
# Update the image object with our new data and extent
ax.images[-1].set(data=self.compute_image(ax.get_xlim(), ax.get_ylim()),
extent=(*ax.get_xlim(), *ax.get_ylim()))
ax.figure.canvas.draw_idle()
md = MandelbrotDisplay()
fig1, (ax_full, ax_zoom) = plt.subplots(1, 2)
ax_zoom.imshow([[0]], origin="lower") # Empty initial image.
ax_zoom.set_title("Zoom here")
rect = Rectangle(
[0, 0], 0, 0, facecolor="none", edgecolor="black", linewidth=1.0)
ax_full.add_patch(rect)
def update_rect(rect, ax): # Let the rectangle track the bounds of the zoom axes.
xlo, xhi = ax.get_xlim()
ylo, yhi = ax.get_ylim()
rect.set_bounds((xlo, ylo, xhi - xlo, yhi - ylo))
ax.figure.canvas.draw_idle()
# Connect for changing the view limits.
ax_zoom.callbacks.connect("xlim_changed", functools.partial(update_rect, rect))
ax_zoom.callbacks.connect("ylim_changed", functools.partial(update_rect, rect))
ax_zoom.callbacks.connect("xlim_changed", md.ax_update)
ax_zoom.callbacks.connect("ylim_changed", md.ax_update)
# Initialize: trigger image computation by setting view limits; set colormap limits;
# copy image to full view.
ax_zoom.set(xlim=(-2, .5), ylim=(-1.25, 1.25))
im = ax_zoom.images[0]
ax_zoom.images[0].set(clim=(im.get_array().min(), im.get_array().max()))
ax_full.imshow(im.get_array(), extent=im.get_extent(), origin="lower")
plt.show()