注意
转到末尾下载完整示例代码。
箱线图的独立计算与绘制#
为给定数据集绘制箱线图包含两个主要操作,它们也可以单独使用:
计算箱线图统计数据:
matplotlib.cbook.boxplot_stats绘制箱线图:
matplotlib.axes.Axes.bxp
因此,ax.boxplot(data)等效于
boxplot和bxp之间的所有样式关键字参数是相同的,并且它们从boxplot传递给bxp。然而,boxplot的 tick_labels 参数在boxplot_stats中转换为一个通用的 labels 参数,因为这些标签与数据相关,并附加到返回的每个数据集字典中。
以下代码演示了这两种方法之间的等效性。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import cbook
np.random.seed(19680801)
data = np.random.randn(20, 3)
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2)
# single boxplot call
ax1.boxplot(data, tick_labels=['A', 'B', 'C'],
patch_artist=True, boxprops={'facecolor': 'bisque'})
# separate calculation of statistics and plotting
stats = cbook.boxplot_stats(data, labels=['A', 'B', 'C'])
ax2.bxp(stats, patch_artist=True, boxprops={'facecolor': 'bisque'})
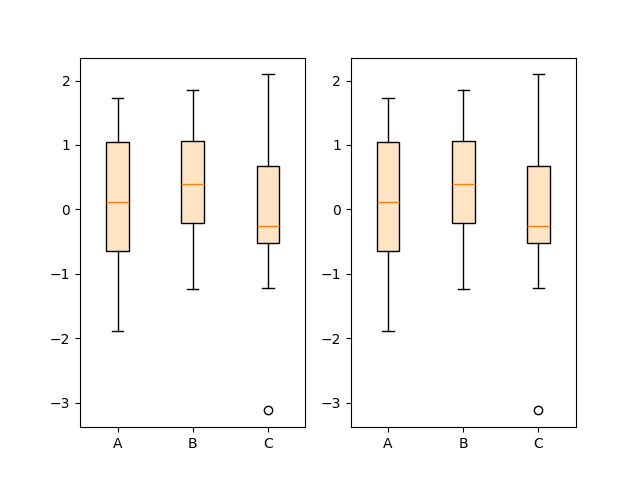
使用这些独立函数可以预先计算统计数据,以防您出于其他目的明确需要它们,或者需要将这些统计数据用于多个图表。
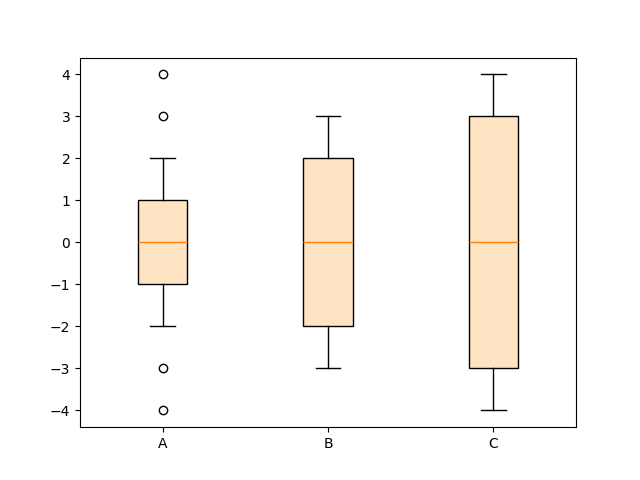
反之,如果您已经拥有统计参数,也可以直接使用bxp函数。
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
stats = [
dict(med=0, q1=-1, q3=1, whislo=-2, whishi=2, fliers=[-4, -3, 3, 4], label='A'),
dict(med=0, q1=-2, q3=2, whislo=-3, whishi=3, fliers=[], label='B'),
dict(med=0, q1=-3, q3=3, whislo=-4, whishi=4, fliers=[], label='C'),
]
ax.bxp(stats, patch_artist=True, boxprops={'facecolor': 'bisque'})
plt.show()
参考
本示例展示了以下函数、方法、类和模块的使用