注意
转到末尾下载完整示例代码。
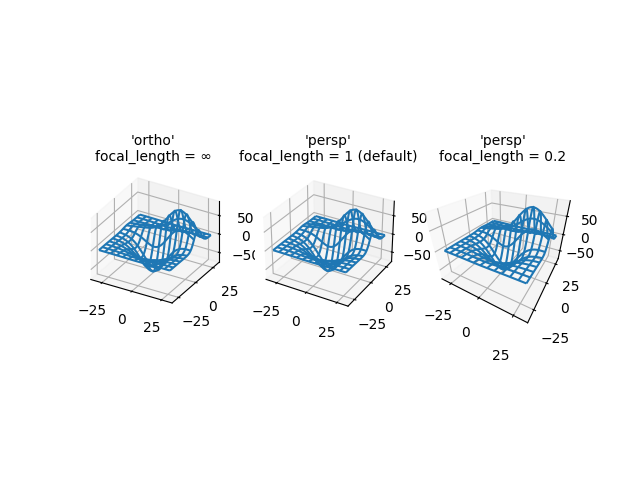
三维图投影类型#
演示了三维图的不同相机投影,以及改变透视投影焦距的影响。请注意,Matplotlib 会对改变焦距引起的“缩放”效果进行校正。
默认焦距1对应于90度的视野(FOV)。焦距在1和无穷大之间增加会“展平”图像,而焦距在1和0之间减小则会夸大透视效果并使图像具有更明显的深度。在极限情况下,经过缩放效果校正后,无穷大的焦距对应于正交投影。
您可以通过以下公式从视野(FOV)计算焦距:
\[1 / \tan (\mathrm{FOV} / 2)\]
反之亦然:
\[\mathrm{FOV} = 2 \arctan (1 / \mathrm{focal length})\]
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import axes3d
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 3, subplot_kw={'projection': '3d'})
# Get the test data
X, Y, Z = axes3d.get_test_data(0.05)
# Plot the data
for ax in axs:
ax.plot_wireframe(X, Y, Z, rstride=10, cstride=10)
# Set the orthographic projection.
axs[0].set_proj_type('ortho') # FOV = 0 deg
axs[0].set_title("'ortho'\nfocal_length = ∞", fontsize=10)
# Set the perspective projections
axs[1].set_proj_type('persp') # FOV = 90 deg
axs[1].set_title("'persp'\nfocal_length = 1 (default)", fontsize=10)
axs[2].set_proj_type('persp', focal_length=0.2) # FOV = 157.4 deg
axs[2].set_title("'persp'\nfocal_length = 0.2", fontsize=10)
plt.show()
脚本总运行时间:(0分钟1.164秒)