注意
转到末尾下载完整示例代码。
修复过多的刻度#
导致刻度行为异常的一个常见原因是传入字符串列表而不是数字或日期时间对象。这在读取逗号分隔的文本文件时很容易在不知不觉中发生。Matplotlib 将字符串列表视为*分类*变量(绘制分类变量),默认情况下为每个类别放置一个刻度,并按照提供的顺序绘制它们。如果不希望这样,解决方案是将字符串转换为数值类型,如下面的示例所示。
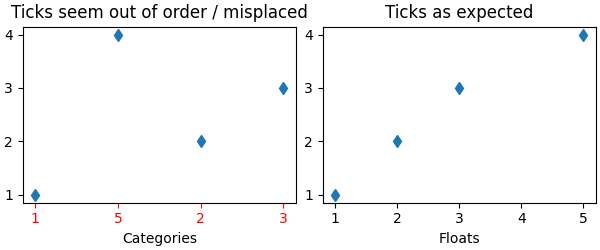
示例 1:字符串可能导致数字刻度顺序异常#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, layout='constrained', figsize=(6, 2.5))
x = ['1', '5', '2', '3']
y = [1, 4, 2, 3]
ax[0].plot(x, y, 'd')
ax[0].tick_params(axis='x', color='r', labelcolor='r')
ax[0].set_xlabel('Categories')
ax[0].set_title('Ticks seem out of order / misplaced')
# convert to numbers:
x = np.asarray(x, dtype='float')
ax[1].plot(x, y, 'd')
ax[1].set_xlabel('Floats')
ax[1].set_title('Ticks as expected')
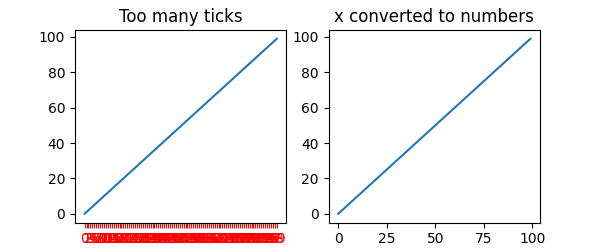
示例 2:字符串可能导致过多的刻度#
如果 *x* 有 100 个元素,且均为字符串,那么我们将得到 100 个(难以辨认的)刻度,解决方案仍然是将字符串转换为浮点数。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(6, 2.5))
x = [f'{xx}' for xx in np.arange(100)]
y = np.arange(100)
ax[0].plot(x, y)
ax[0].tick_params(axis='x', color='r', labelcolor='r')
ax[0].set_title('Too many ticks')
ax[0].set_xlabel('Categories')
ax[1].plot(np.asarray(x, float), y)
ax[1].set_title('x converted to numbers')
ax[1].set_xlabel('Floats')
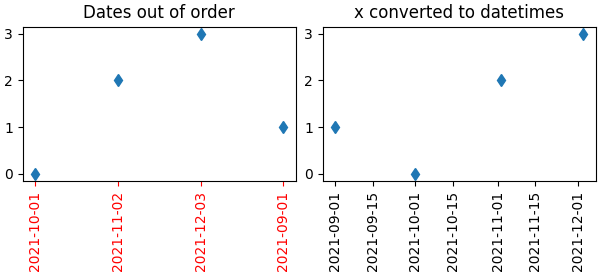
示例 3:字符串可能导致日期时间刻度顺序异常#
常见情况是当从 CSV 文件读取日期时,需要将它们从字符串转换为日期时间对象,以获得正确的日期定位器和格式化器。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2, layout='constrained', figsize=(6, 2.75))
x = ['2021-10-01', '2021-11-02', '2021-12-03', '2021-09-01']
y = [0, 2, 3, 1]
ax[0].plot(x, y, 'd')
ax[0].tick_params(axis='x', labelrotation=90, color='r', labelcolor='r')
ax[0].set_title('Dates out of order')
# convert to datetime64
x = np.asarray(x, dtype='datetime64[s]')
ax[1].plot(x, y, 'd')
ax[1].tick_params(axis='x', labelrotation=90)
ax[1].set_title('x converted to datetimes')
plt.show()
脚本总运行时间: (0 分钟 2.115 秒)