注意
跳转到末尾以下载完整示例代码。
坐标轴刻度#
每个 Axes 上的 x 和 y 轴都有默认的刻度“定位器”("locators")和“格式器”("formatters"),它们取决于所使用的刻度(参见 坐标轴刻度)。可以通过高级方法(如 set_xticks)自定义刻度及其标签,或者直接在轴上设置定位器和格式器。
手动定位和格式化#
自定义刻度位置和格式的最简单方法是使用 set_xticks 和 set_yticks。这些方法可以用于主要刻度或次要刻度。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.ticker as ticker
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(5.4, 5.4), layout='constrained')
x = np.arange(100)
for nn, ax in enumerate(axs):
ax.plot(x, x)
if nn == 1:
ax.set_title('Manual ticks')
ax.set_yticks(np.arange(0, 100.1, 100/3))
xticks = np.arange(0.50, 101, 20)
xlabels = [f'\\${x:1.2f}' for x in xticks]
ax.set_xticks(xticks, labels=xlabels)
else:
ax.set_title('Automatic ticks')
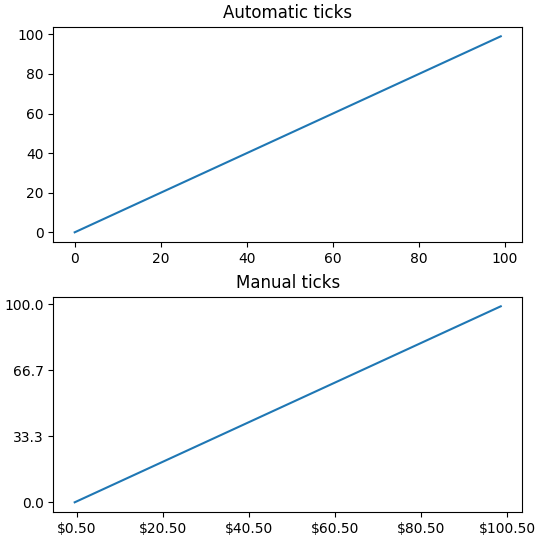
请注意,labels 参数的长度必须与用于指定刻度的数组长度相同。
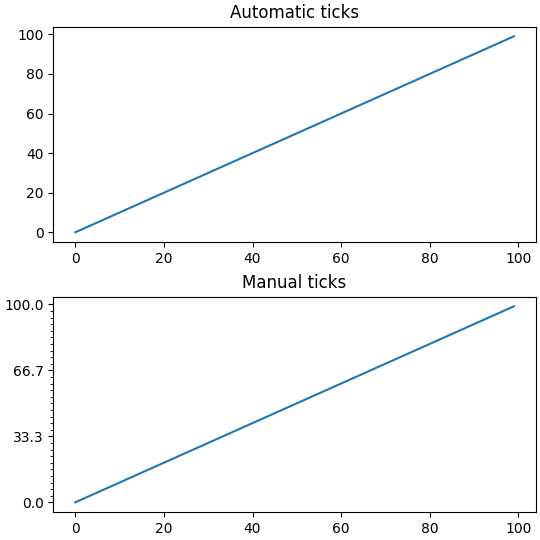
默认情况下,set_xticks 和 set_yticks 作用于坐标轴的主要刻度,但也可以添加次要刻度
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(5.4, 5.4), layout='constrained')
x = np.arange(100)
for nn, ax in enumerate(axs):
ax.plot(x, x)
if nn == 1:
ax.set_title('Manual ticks')
ax.set_yticks(np.arange(0, 100.1, 100/3))
ax.set_yticks(np.arange(0, 100.1, 100/30), minor=True)
else:
ax.set_title('Automatic ticks')
定位器和格式器#
如上所述手动设置刻度对于特定的最终绘图效果很好,但当用户与 Axes 交互时,它们不会自适应。在更低的层面,Matplotlib 有 Locators,它们旨在根据坐标轴当前的视图限制自动选择刻度,以及 Formatters,它们旨在自动格式化刻度标签。
Matplotlib 提供的定位器完整列表可在 刻度定位 找到,格式器可在 刻度格式化 中找到。
def setup(ax, title):
"""Set up common parameters for the Axes in the example."""
# only show the bottom spine
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.NullLocator())
ax.spines[['left', 'right', 'top']].set_visible(False)
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
ax.tick_params(which='major', width=1.00, length=5)
ax.tick_params(which='minor', width=0.75, length=2.5)
ax.set_xlim(0, 5)
ax.set_ylim(0, 1)
ax.text(0.0, 0.2, title, transform=ax.transAxes,
fontsize=14, fontname='Monospace', color='tab:blue')
fig, axs = plt.subplots(8, 1, layout='constrained')
# Null Locator
setup(axs[0], title="NullLocator()")
axs[0].xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.NullLocator())
axs[0].xaxis.set_minor_locator(ticker.NullLocator())
# Multiple Locator
setup(axs[1], title="MultipleLocator(0.5)")
axs[1].xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(0.5))
axs[1].xaxis.set_minor_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(0.1))
# Fixed Locator
setup(axs[2], title="FixedLocator([0, 1, 5])")
axs[2].xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.FixedLocator([0, 1, 5]))
axs[2].xaxis.set_minor_locator(ticker.FixedLocator(np.linspace(0.2, 0.8, 4)))
# Linear Locator
setup(axs[3], title="LinearLocator(numticks=3)")
axs[3].xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.LinearLocator(3))
axs[3].xaxis.set_minor_locator(ticker.LinearLocator(31))
# Index Locator
setup(axs[4], title="IndexLocator(base=0.5, offset=0.25)")
axs[4].plot(range(0, 5), [0]*5, color='white')
axs[4].xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.IndexLocator(base=0.5, offset=0.25))
# Auto Locator
setup(axs[5], title="AutoLocator()")
axs[5].xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.AutoLocator())
axs[5].xaxis.set_minor_locator(ticker.AutoMinorLocator())
# MaxN Locator
setup(axs[6], title="MaxNLocator(n=4)")
axs[6].xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MaxNLocator(4))
axs[6].xaxis.set_minor_locator(ticker.MaxNLocator(40))
# Log Locator
setup(axs[7], title="LogLocator(base=10, numticks=15)")
axs[7].set_xlim(10**3, 10**10)
axs[7].set_xscale('log')
axs[7].xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.LogLocator(base=10, numticks=15))
plt.show()

类似地,我们可以为每个轴上的主要刻度和次要刻度指定“格式器”("Formatters")。
刻度格式通过函数 set_major_formatter 或 set_minor_formatter 进行配置。它接受
一个格式字符串,它隐式地创建一个
StrMethodFormatter。一个函数,隐式地创建一个
FuncFormatter。一个
Formatter子类的实例。最常见的是NullFormatter:刻度上无标签。StrMethodFormatter:使用字符串str.format方法。FormatStrFormatter:使用 % 样式格式化。FuncFormatter:通过函数定义标签。FixedFormatter:明确设置标签字符串。ScalarFormatter:标量的默认格式器:自动选择格式字符串。PercentFormatter:将标签格式化为百分比。
完整列表请参见 刻度格式化。
def setup(ax, title):
"""Set up common parameters for the Axes in the example."""
# only show the bottom spine
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.NullLocator())
ax.spines[['left', 'right', 'top']].set_visible(False)
# define tick positions
ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(1.00))
ax.xaxis.set_minor_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(0.25))
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom')
ax.tick_params(which='major', width=1.00, length=5)
ax.tick_params(which='minor', width=0.75, length=2.5, labelsize=10)
ax.set_xlim(0, 5)
ax.set_ylim(0, 1)
ax.text(0.0, 0.2, title, transform=ax.transAxes,
fontsize=14, fontname='Monospace', color='tab:blue')
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8), layout='constrained')
fig0, fig1, fig2 = fig.subfigures(3, height_ratios=[1.5, 1.5, 7.5])
fig0.suptitle('String Formatting', fontsize=16, x=0, ha='left')
ax0 = fig0.subplots()
setup(ax0, title="'{x} km'")
ax0.xaxis.set_major_formatter('{x} km')
fig1.suptitle('Function Formatting', fontsize=16, x=0, ha='left')
ax1 = fig1.subplots()
setup(ax1, title="def(x, pos): return str(x-5)")
ax1.xaxis.set_major_formatter(lambda x, pos: str(x-5))
fig2.suptitle('Formatter Object Formatting', fontsize=16, x=0, ha='left')
axs2 = fig2.subplots(7, 1)
setup(axs2[0], title="NullFormatter()")
axs2[0].xaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.NullFormatter())
setup(axs2[1], title="StrMethodFormatter('{x:.3f}')")
axs2[1].xaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.StrMethodFormatter("{x:.3f}"))
setup(axs2[2], title="FormatStrFormatter('#%d')")
axs2[2].xaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.FormatStrFormatter("#%d"))
def fmt_two_digits(x, pos):
return f'[{x:.2f}]'
setup(axs2[3], title='FuncFormatter("[{:.2f}]".format)')
axs2[3].xaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.FuncFormatter(fmt_two_digits))
setup(axs2[4], title="FixedFormatter(['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F'])")
# FixedFormatter should only be used together with FixedLocator.
# Otherwise, one cannot be sure where the labels will end up.
positions = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
labels = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F']
axs2[4].xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.FixedLocator(positions))
axs2[4].xaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.FixedFormatter(labels))
setup(axs2[5], title="ScalarFormatter()")
axs2[5].xaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.ScalarFormatter(useMathText=True))
setup(axs2[6], title="PercentFormatter(xmax=5)")
axs2[6].xaxis.set_major_formatter(ticker.PercentFormatter(xmax=5))

刻度样式(刻度参数)#
可以通过在轴上找到单个 Tick 来低级别控制刻度的外观。然而,通常最简单的方法是使用 tick_params 一次性更改所有对象。
tick_params 方法可以改变刻度的属性:
长度
方向(在框架内或框架外)
颜色
宽度和长度
以及刻度是否绘制在 Axes 的底部、顶部、左侧或右侧。
它还可以控制刻度标签的
标签大小(字体大小)
标签颜色(标签的颜色)
标签旋转
labelbottom, labeltop, labelleft, labelright
此外,还有一个 pad 关键字参数,它指定了刻度标签与刻度之间的距离。
最后,可以设置网格线样式:
grid_color
grid_alpha
grid_linewidth
grid_linestyle
所有这些属性都可以限定于一个轴,并且可以仅应用于主要刻度或次要刻度。
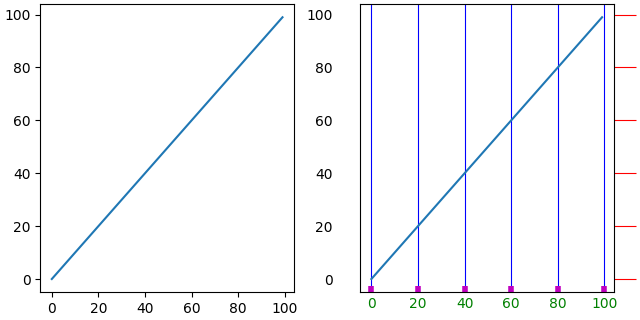
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(6.4, 3.2), layout='constrained')
for nn, ax in enumerate(axs):
ax.plot(np.arange(100))
if nn == 1:
ax.grid('on')
ax.tick_params(right=True, left=False, axis='y', color='r', length=16,
grid_color='none')
ax.tick_params(axis='x', color='m', length=4, direction='in', width=4,
labelcolor='g', grid_color='b')
脚本总运行时间:(0 分钟 7.352 秒)